Genital boils vs Herpes warts: Their Differences
Unable to tell the differences between vaginal boil and herpes? This article explains how you can tell them apart.
Written By
Covenant OtafuHealth Writer | Copywriter
Reviewed By
Azuka Chinweokwu EzeikeMedical Doctor (MBBS), MSc(PH) | Consultant Obstetrician & Gynecologist
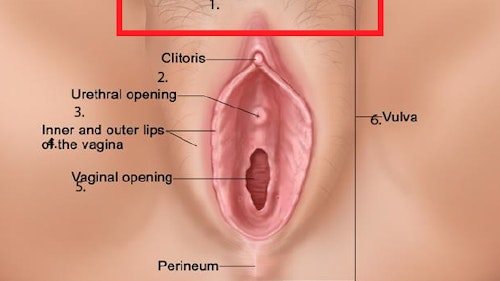
Key takeaways:
- Genital herpes is a viral disease that causes blisters in and around the genital region. In contrast, genital boils (also commonly referred to as vaginal boils) are caused by bacterial infections.
- Genital herpes presents as blisters that eventually form painful sores, while vaginal boils are pus-filled bumps that cause pain and swelling.
- Genital herpes often requires antiviral medication, while vaginal boils usually resolve with home treatments such as a warm compress and sitz bath.
Vaginal boils are pus-filled bumps of varying sizes that occur in the mons pubis (the hair-covered flesh over the pubic bone), the vagina lips, and sometimes the groin area above the pubic bone. A bacterial infection causes vaginal boils. They are usually not very serious and are quite common among women.
Genital herpes, on the other hand, is a group of blisters that can occur on your genitals, and they contain clear or white fluid when ruptured. This viral infection is sexually transmitted and manifests with various symptoms as outlined below.
Both the vaginal boils and genital herpes release fluids when ruptured. However, they have different causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
Genital herpes - Definition
Genital herpes is a viral infection that is transmitted through skin-to-skin contact. It is caused by the Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV), which causes fluid-filled sores or blisters around the genital areas. There are two types of HSV - HSV I and HSV II.
- HSV I: The HSV I causes cold sores in the mouth without any other symptoms. However, it can cause genital herpes through oral sex with an infected person.
- HSV II: Causes genital herpes, which appear as sores in the genital area such as the vagina, vulva, cervix, and anus. It is mainly transmitted through sex.
Transmission of genital herpes
When HSV II gets into the body through skin abrasions or mucosal membranes—moist tissue that lines some organs and cavities, such as the mouth, nose, and genital areas—it causes genital herpes. It can be transmitted even when an infected person has no sores, although the risk is higher when active sores exist.
Because this virus is found in bodily fluids like saliva, vaginal discharge, and semen, transmission is primarily by direct skin-to-skin contact during sexual intercourse with or without ejaculation.
Infants can acquire HSV II from infected mothers during birth and HSV I via kissing. People with HSV I or II may be asymptomatic but infectious and can transmit these viruses unknowingly.
Causes of boil in the genital area
When Staphylococcus aureus, a type of bacteria that naturally lives on the skin, gets into hair roots, an infection can occur. Cuts and abrasions, such as those incurred during shavings, are also ways staph and other bacteria can enter the body to cause infections.
Medical conditions such as hidradenitis suppurativa, also known as acne inversa, can cause recurring vaginal boils.
Symptoms of genital boils
Genital boils typically cause the following symptoms:
- Bumps with whitish or yellow tips that contain pus
- Pain and tenderness at the site of the boil
- Discomfort while walking, sitting, or standing
Symptoms of genital herpes
Most times, people with genital herpes are asymptomatic or have mild symptoms like little bumps that can easily be mistaken for a pimple. Symptoms of genital herpes are called outbreaks. An outbreak is a blister or group of blisters that ooze clear yellow fluid.
Some common areas to find these blisters include:
- Areas around the anus and,
- Around the vagina
If experiencing your first outbreak of genital herpes, you may notice:
- Flu-like symptoms such as body aches, fever, and sore throat
- Burning or itching sensations that often start before the appearance of blisters
- Swollen glands or lymph nodes around the area
Genital herpes is a lifelong infection unless treated; subsequent outbreaks are usually less intense and painful than the first.
Genital herpes blisters compared to vaginal boils
Genital herpes manifests as white, yellow, or red translucent (semi-transparent) blisters against a background of visibly irritated skin. These blisters range between 1 and 3 millimeters, are irregularly shaped, and feel squishy when touched.
Genital boils, on the other hand, are red or discolored bumps with a white or yellow tip. They start the size of a pimple and then get bigger over time. Initially, a boil feels firm to the touch, but when it gets larger, it may become tender.
Treatment for genital herpes
Your doctor may prescribe an antiviral agent like acyclovir, which stops the replication of the virus and alleviates any symptoms you may be experiencing. Factors like whether it’s a primary or recurrent infection will affect the dosage and duration of use of antiviral medication.4
Over-the-counter (OTC) painkillers and home remedies like sitz baths can also help reduce the intensity of symptoms during an outbreak.
Treatment for genital boils
Genital boils often don't require medication. They usually resolve with home treatments. Home treatments include:
- Sitz bath
- Using a warm compress
- Wearing comfortable, breathable underwear and pants.
Your doctor may prescribe antibiotics if the boils persist even after home treatments.
Genital Herpes | Genital Boils | |
|---|---|---|
Causes | Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV). | Predominantly Staphylococcus aureus bacteria. |
Mode of Transmission | Vaginal, anal, and oral sex, and close skin-to-skin contact. | Direct skin-to-skin contact, and using infected personal items like towels. |
Symptoms | Blisters that form painful sores on the genitals, groin area, anus, and mouth. Flu-like symptoms and swollen lymph nodes might be present. | Pus-filled bumps on and around the vagina. |
Appearance and Feel | Blisters appear, usually in clusters. They are irregularly shaped and appear reddish, pinkish, or darker than the surrounding area. They are between 1-3 millimeters in size. | At the developing stage, it looks similar to a pimple. With time, it grows into a bigger round bump with a whitish or yellowish pus-filled tip. |
Treatment | Antiviral drug prescribed by a doctor | Home treatments. Your doctor may also prescribe antibiotics. |
Genital Herpes | Genital Boils | |
|---|---|---|
Causes | Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV). | Predominantly Staphylococcus aureus bacteria. |
Mode of Transmission | Vaginal, anal, and oral sex, and close skin-to-skin contact. | Direct skin-to-skin contact, and using infected personal items like towels. |
Symptoms | Blisters that form painful sores on the genitals, groin area, anus, and mouth. Flu-like symptoms and swollen lymph nodes might be present. | Pus-filled bumps on and around the vagina. |
Appearance and Feel | Blisters appear, usually in clusters. They are irregularly shaped and appear reddish, pinkish, or darker than the surrounding area. They are between 1-3 millimeters in size. | At the developing stage, it looks similar to a pimple. With time, it grows into a bigger round bump with a whitish or yellowish pus-filled tip. |
Treatment | Antiviral drug prescribed by a doctor | Home treatments. Your doctor may also prescribe antibiotics. |
Tips for preventing genital herpes
To prevent genital herpes:
- Practice safe sex by using a condom during vaginal, anal, and oral sex. Infection is still possible if the condom doesn’t cover the infected part.
- Avoid sharing sex toys and clean them properly before use.
- Avoid having sex with your partner if they have blisters, sores, or any itching that could be warning signs of an outbreak.
Tips for preventing genital boils
To reduce your risk of genital boils:
- Avoid vaginal, oral, or anal sex when your partner has genital boils.
- Avoid sharing personal items like underwear, towels, razors, and sex toys.
- Dress genital cuts and wounds properly and with antiseptic to prevent infection.
- Practice personal hygiene to reduce the risk of developing genital boils.
- Shave your pubic hair toward hair growth to prevent in-grown hairs and the risk of developing a boil.
When to seek medical attention
Genital herpes can cause serious complications, especially in people with reduced immunity. You should seek medical attention if:
- You’re experiencing your first outbreak
- Subsequent outbreaks are more or equally as painful as the first
- You are pregnant
- You have flu-like symptoms
- The blisters and sores are extensive
For genital boils, seek medical attention if:
- You have a fever
- The boil is large and painful
- The boil persists after two weeks of home treatments
- You’ve observed signs of an infection, like redness or swollen lymph nodes around the boil.
Conclusion
Genital herpes and genital boils can look similar at some point in their development. However, major differences exist in their causes, modes of transmission, symptoms, and treatment.
It is important to note that HSV currently has no cure. Management with antiviral medication and avoiding potential triggers are the only ways to reduce outbreaks.
HSV lives inside nerve cells and alternates between being active and inactive. Common triggers that can activate the virus include sun exposure, injury, and stress.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Can boils be mistaken for herpes?
Are pimples on the pubic area normal?
What are the first signs of genital herpes?