Ingrown hair (razor bumps) vs. herpes: What is the difference?
It is normal to freak out when you notice bumps on your skin, especially around the genitals. But the bumps may not be caused by herpes. They may simply be razor bumps caused by ingrown hair.
Written By
Oluoma Vivian AnekeHuman Anatomist
Reviewed By
Grace EnehMedical Doctor (MBBS) | Consultant Neurologist
Key takeaways:
- Ingrown hair and herpes differ in causes, appearance and mode of treatment.
- Ingrown hair causes bumps that appear after shaving, while herpes is a condition caused by a virus that causes bumps and sores on the skin.
- Both ingrown hair and herpes can be treated using home remedies and topical creams.
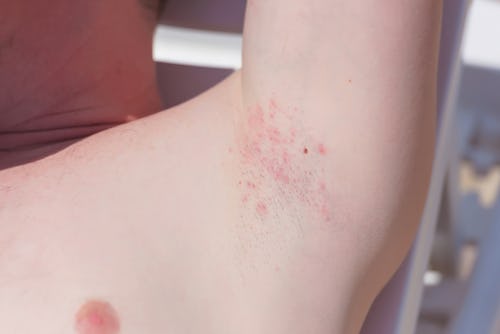
Razor bumps or ingrown hair are skin issues that occur after shaving. Both terms describe cases where hair grows back into the skin after shaving, causing red bumps. Razor bumps can appear on any body part that can be shaved. The most common places include the underarms, groin, legs, and face.
Herpes, on the other hand, is a viral infection that causes symptoms that are visible on the skin. Often, herpes and razor bumps are mistaken for each other because they both cause bumps or sores to appear on the skin. However, they are in no way related. So, what differentiates them?
This article will explore herpes vs ingrown hairs (differences between herpes and ingrown hair), their causes, how to identify them, and when to visit your doctor.
Ingrown hair (razor bumps) vs herpes: The differences
The major difference between herpes and ingrown hair is in their causes. While herpes is a sexually transmitted disease that often occurs after a person comes in sexual contact with an infected person, ingrown hair only occurs when hair grows back into the skin after shaving.
Herpes and ingrown hair also differ in their signs and symptoms. Below is a table highlighting the differences between herpes and ingrown hair.
Herpes | Razor bump or Ingrown Hair | |
|---|---|---|
Location | Herpes occurs mainly in the genital or rectal areas and also around the oral region | Razor bumps are found anywhere that hair grows and not limited to the genital and oral areas |
Time of occurrence | Herpes can occur at any time so long as a person is infected with the herpes simplex virus | Ingrown hairs or razor bumps occur mainly after shaving |
Treatment | Herpes does not have a permanent cure, it is a lifelong infection that can only be managed or suppressed | Ingrown hair or razor bumps can be permanently treated using both topical medications and natural remedies |
Mode of treatment | Herpes cannot be treated or managed at home; it has to be treated by a doctor. | Ingrown hairs can be treated using home remedies or over the counter products. |
Appearance | Herpes always appear as clusters of sores and blisters or brown crusts after the blisters rupture, visible on top of the skin affected | Ingrown hair or razor bumps are small bumps under the skin. They often look like small reddish rashes |
Severity of pain | Herpes always causes severe pain in the areas affected | Ingrown hairs causes pain mostly when you apply pressure in the affected area |
Frequency of occurrence | Herpes infection can cause regular outbreaks. People with HSV 1 might have up to 2 outbreaks a year, while HSV 2 presents more frequent outbreaks. | Ingrown hairs barely occur at random. They only get triggered when hair grows back into the skin after shaving. |
Causes of ingrown hair (or razor bumps)
Ingrown hair occurs when the sharp edge of the hair grows back into the skin after shaving. The hairs become irritating to the skin, and to try to ward them off, the skin sends out some inflammatory cells.
The inflammatory cells then cause the appearance of red bumps (also called razor bumps) in the affected area. The main things that cause the hair to grow back are when the razor cuts through the skin or when the hair is too curly.
By learning how to shave without getting razor bumps, you can reduce the chances of such an occurrence.
How to identify razor bumps caused by ingrown hairs
Razor bumps form small rounded rashes and is usually not accompanied symptoms like fever and headache
Razor bumps can appear like any other bumps. They are not hidden and are easy to identify.
The most typical symptoms of razor bumps include:
- Small rounded rashes in the jaw, armpits, genital area, and everywhere hair grows in the body
- Darkening of the skin in the affected area
- The feeling of tenderness or softness in the affected area when touched
- Itching and burning sensation
- Pus-filled lesions
- Red or inflamed bumps
Causes of herpes
Herpes is a viral infection caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV). Herpes causes sores or blisters in areas like the mouth and genitals.
There are two types of herpes - HSV type 1 and HSV type 2.
HSV type 1 leads to oral herpes and affects the mouth and skin around the mouth region. It also affects the genital area.
HSV type 2 causes genital herpes3 and is sexually transmitted.
However, oral herpes is more easily diagnosed than genital herpes because most people infected with HSV -2 do not have the typical symptoms.4
People contract HSV 1 and HSV 2 in different ways.
The common ways HSV type 1 can be contracted are:
- Skin contact - Herpes can be transmitted through skin-to-skin contact. HSV present on the moist skin of the mouth and genitals can be transmitted from one person to another
- Through sharing food utensils, lip balms, or razors with another person with cold sores
- Any activity that exposes you to an infected person's saliva, like lipsticks and make-up brushes or mouth-to-mouth contact1
- Having oral sex with a person who has the oral herpes virus
HSV type 2 can be contracted by:
- Having sex without protection (this is the easiest way to get genital herpes)
- Sharing sex toys with others who have the infection
- Open sores during breastfeeding
- Engaging in oral or genital sex with someone infected with herpes
How to identify herpes
Mouth sores caused by herpes simpex virus
Most of the time, there are no symptoms when herpes first starts, and sometimes the virus can stay dormant in the body. However, the easiest way to identify herpes is through its common symptoms. Some of the symptoms include:
- Cold sores (sometimes filled with fluid) or fever blisters in the lips, tongue, or mouth
- Sores on your genitals or around your anus
- Itching, tingling, or burning sensation
- Fever
- Muscle aches
- Painful urination
- A repeated outbreak of the sores
- Headache
When to see a doctor for bumps or sores in the genital area
Some genital sores or bumps are harmless, e.g., razor bumps caused by ingrown hair. With some home remedies, razor bumps can be treated.
However, there are some genital bumps or sores that call for concern and will require you to meet with your medical doctor. Examples of these sores are the ones caused by herpes, syphilis, and some other sexually transmitted diseases.
If you have a bump or sore in your genital area and any of the following signs, you should immediately see your doctor:
- Bumps that bleed
- Abnormal discharge
- Destruction of the genital tissues
- Swelling in the genital area
- Pelvic pain
- Sores in the groin
- Burning sensation in the genital area
- A small insect crawling through the pubic hair
- Pain during intercourse
- Pain when urinating
Wrap up
Bumps or sores in the genital area can be uncomfortable. In some cases (such as razor bumps), they may not cause serious complications. But, in other cases (such as STDs), bumps and sores can mean an underlying health condition.
Due to the sensitivity of the genital area, it is advisable to treat bumps in such areas with caution. As a result, if you notice any unusual sore or bump in the genital area, especially if it is not an after-shave effect, you should see your doctor right away.